科技工作者之家
科技工作者之家APP是专注科技人才,知识分享与人才交流的服务平台。
科技工作者之家 2019-04-16
来源:ScienceAAAS
人类首次看见黑洞的样子
 This image reveals the black hole at the center of Messier 87, a massive galaxy in the nearby Virgo galaxy cluster. The black hole resides 55 million light-years from Earth and has a mass 6.5 billion times that of the sun.
This image reveals the black hole at the center of Messier 87, a massive galaxy in the nearby Virgo galaxy cluster. The black hole resides 55 million light-years from Earth and has a mass 6.5 billion times that of the sun.
This week, astronomers revealed the first image ever of a black hole—the gargantuan mass at the heart of nearby galaxy Messier 87. The image, a ring of fire surrounding the blackest of shadows, is a powerful confirmation of Albert Einstein’s theory of gravity, or general relativity, which was used to predict black holes 80 years ago. It is also a feat for the team of more than 200 scientists who toiled for years to produce the image by combining signals from eight separate radio observatories spanning the globe.
相信亚特兰蒂斯?这些考古学家想把你带回科学界
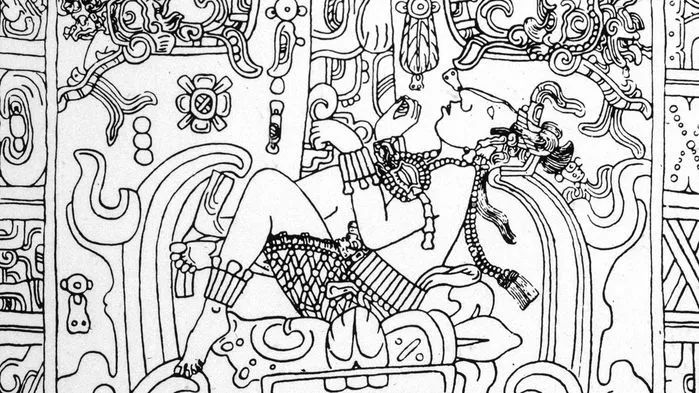
Mayan King K’inich Janaab’ Pakal is not taking off in a spaceship in this image from his seventh century sarcophagus, but falling into the underworld.
Archaeologists alarmed by the rise of what they call “pseudoarchaeology” are taking to Twitter, blogs, podcasts, and YouTube to debunk false claims about ancient civilizations, including claims that aliens helped build the Egyptian and Mayan pyramids, refugees from Atlantis brought advanced technology to cultures around the world, and European immigrants were the original inhabitants of North America. Researchers say almost all such claims depend on the racist assumption that ancient non-European societies weren’t capable of inventing sophisticated architecture, calendars, math, and astronomy on their own.
大气化学家能拯救停滞的人类信息素探索吗?
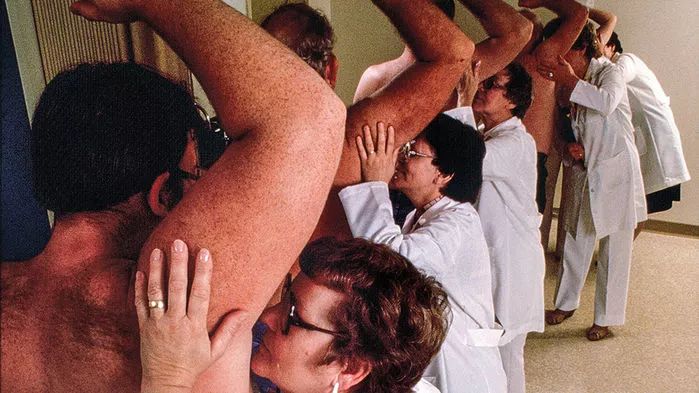 Decades of research have failed to yield any human pheromones.
Decades of research have failed to yield any human pheromones.
For decades, scientists have searched in vain for a human pheromone—a chemical signal in human body odor. Now, atmospheric chemists are using techniques for parsing atmospheric particles to breathe new life into the stalled field of inquiry. Tools of their trade, such as proton transfer reaction mass spectrometry, could aid in the hunt for pheromones—measuring the changing concentrations of compounds in real time as people react to different situations.
解密的U-2间谍飞机照片是航空考古的一大福音
 An aerial shot of Aleppo, Syria, taken by a U-2 spy plane in 1959
An aerial shot of Aleppo, Syria, taken by a U-2 spy plane in 1959
E. Hammer et al.,Advances in Archaeological Practice10.1017 (2019)
Investigating lost historical sites, like those destroyed by the Islamic State group in Iraq and Syria, is a major challenge for archaeologists. Now, researchers are using declassified high-resolution photos taken by U.S. spy planes to reconstruct archaeological sites lost to development and war in recent decades. Declassified in 1997, the photos were taken by U-2 spy planes that flew over the Middle East, the former Soviet Union, Eastern Europe, China, South America, and Cuba during the 1950s and 1960s.
试图弄清楚大脑错综复杂的网络的物理学家

Danielle Bassett with a representation of the brain's structural connections, created in her lab from MRI data.
来源:Science-AAAS ScienceAAAS
原文链接:http://mp.weixin.qq.com/s?__biz=MzI3NDY3NzQ2Mg==&mid=2247486816&idx=1&sn=ffea411fe661508b0f3f08a953f38a1b&chksm=eb1126d9dc66afcf323840b8354e3c45a1e1532c3d13f160f9e8d20dbb064029ce71e7c39e51&scene=27#wechat_redirect
版权声明:除非特别注明,本站所载内容来源于互联网、微信公众号等公开渠道,不代表本站观点,仅供参考、交流、公益传播之目的。转载的稿件版权归原作者或机构所有,如有侵权,请联系删除。
电话:(010)86409582
邮箱:kejie@scimall.org.cn