科技工作者之家
科技工作者之家APP是专注科技人才,知识分享与人才交流的服务平台。
科技工作者之家 2020-09-08
来源:X一MOL资讯
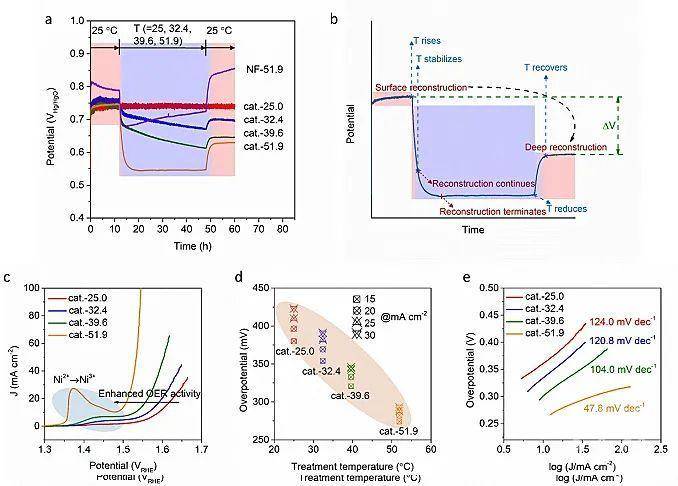
Figure 1 a) Chronopotentiometric measurements of NiMoO4 pre-catalyst and nickel foam (NF) at 10 mA cm-2 in 1 M KOH with solution temperatures of T. In detail, the initial 0-12 h stage was tested at 25.0 ℃, and the next 12-48 h stage was tested at T ℃ (T = 25.0, 32.4, 39.6, 51.9), and the final 48-60 h stage was tested at 25.0 ℃. The finally obtained catalysts are denoted as cat.-T for subsequent performance evaluation. For NF-T sample, T is 51.9. b) Schematic diagram for the temperature-dependent potential curve, which associates with the thermal-induced reconstruction results. The reduced potential ΔV is based on the difference value of potentials at 60 and 12 h in (a). c-e) LSV curves, the corresponding overpotentials, and Tafel values of cat.-T tested at 25.0 ℃, respectively.
(2)非原位物相/微结构表征及原位高低温拉曼(Figure 2):发现在常温下仅发生表面重构的钼酸镍前催化剂,在工业高温下可以发生全部相转变(全重构)并形成羟基氧化物催化活性物种,实现了催化组分的高效利用;高温促使催化剂活性提升归因于更多的高活性催化物种的产生;
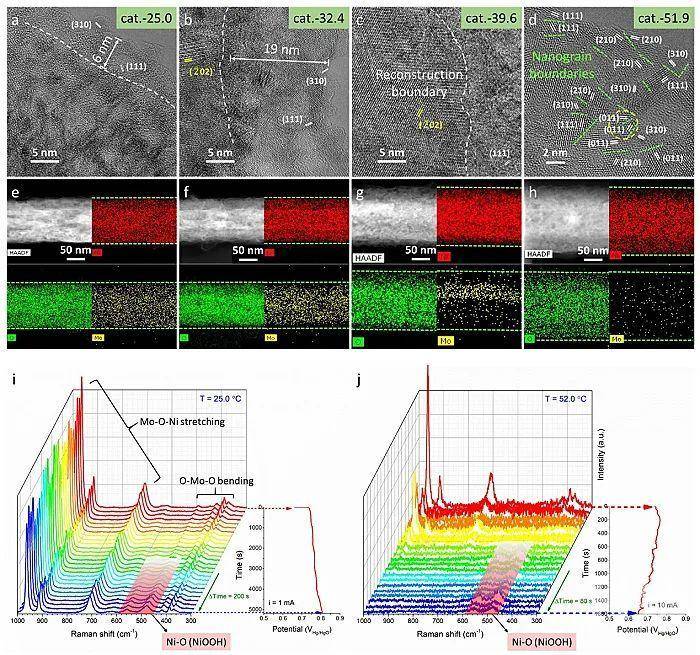
Figure 2 a-d) HRTEM and e-h) HAADF-STEM images and the corresponding elemental mappings of cat.-T (T = 25.0, 32.4, 39.6, 51.9). The white dotted lines in (a-c) represent the obviously observed reconstruction boundary. i) In situ low-temperature Raman spectra and the corresponding chronopotentiometric curve of NiMoO4 pre-catalyst with the interval time of 200 s in 1 M KOH at 25.0 ℃. j) In situ high-temperature Raman spectra and the corresponding chronopotentiometric curve of NiMoO4 pre-catalyst with the interval time of 80 s in 1 M KOH at 52.0 ℃.
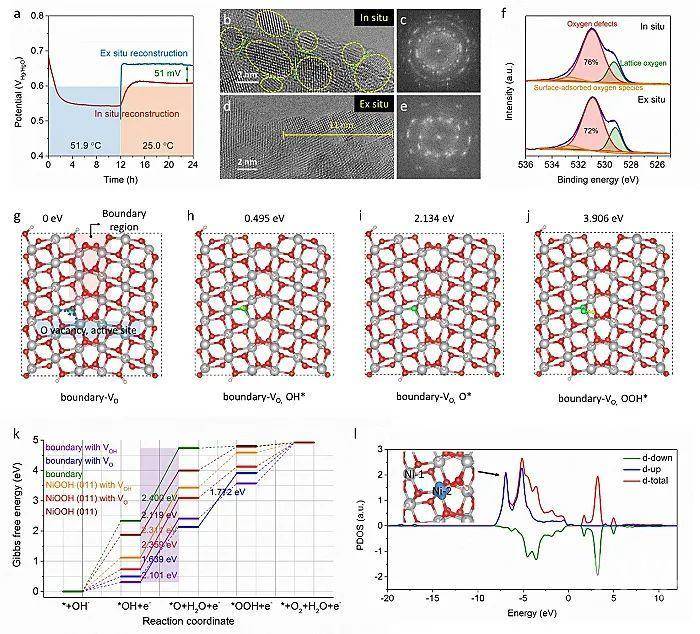
(3)重构程度(Figure 3):当前涉及有限重构机理的报道很少,部分报道认为有限的电子/离子传输或金属浸出引诱的晶格氧氧化等电子结构的调制,是导致有限重构的主要原因。本工作发现,致密重构层是导致钼酸镍在常温测试时仅发生表面重构的主要原因;而高温环境加速了Mo物种的浸出和使得重构层变得疏松,因而促进了电解液的深度浸润和加深了重构程度;

Figure 3 a) HAADF-STEM image of NiMoO4 pre-catalyst after chronopotentiometric measurement at 10 mA cm-2 at 25.0 ℃ for 12 h. b) HAADF-STEM image of NiMoO4 pre-catalyst after chronopotentiometric measurement at 10 mA cm-2 at 25.0 ℃ for 12 h and then rising to 51.9 ℃. c) HAADF-STEM image and the corresponding elemental mappings of sample in (b), showing the dissolution of Mo species on the surface. d) Schematic diagram for the two reconstruction results of NiMoO4 pre-catalyst under low-/high-temperature electro-oxidation conditions.
(4)重构顺序(Figure 4):发现高温碱刻蚀-重构的同步进行,是形成小颗粒和丰富晶界的原因。如果在电氧化重构前先进行碱刻蚀反应,则得到的催化剂是具有较高结晶性和较少晶界的片状结构,进而导致较低的催化活性。基于理论分析,也进一步证明了晶界-氧空位在高OER动力学方面的重要角色;
来源:X-molNews X一MOL资讯
原文链接:http://mp.weixin.qq.com/s?__biz=MzAwOTExNzg4Nw==&mid=2657659076&idx=4&sn=8a04f02230224dd5b26c69e333020a58&chksm=80f88114b78f08028d7b895f8b203acaf60ab33bc9b1bcfccc29b9d16f6cd985efc947fdb5cc&scene=27#wechat_redirect
版权声明:除非特别注明,本站所载内容来源于互联网、微信公众号等公开渠道,不代表本站观点,仅供参考、交流、公益传播之目的。转载的稿件版权归原作者或机构所有,如有侵权,请联系删除。
电话:(010)86409582
邮箱:kejie@scimall.org.cn

电解水低成本高活性双功能催化剂!
JACS封面:新型低成本电解水催化剂系列进展!
行业关注 | 国内燃料电池催化剂及电解水制氢催化剂实现突破
中国科大研制白铁矿型电解水制氢电催化剂

这种二维材料虽易自氧化,但或可作为高效催化剂
中国科大在酸性电解水催化剂开发上取得重要进展
南开大学教授周其林院士:以化学“催化”育人之美



中国科大酸性电解水单原子分散催化剂调控研究取得进展



大连化物所开发出高效碱性电解水单原子合金催化剂

冯小明:二十年磨一剑,耐得住寂寞的科学家 | 2018年未来科学大奖获奖人