科技工作者之家
科技工作者之家APP是专注科技人才,知识分享与人才交流的服务平台。
科技工作者之家 2019-02-27
1自旋电子学材料、物理与器件研究进展
报告人:韩秀峰,中科院物理研究所
时间:2月28日(周四)18:30
单位:中国科学院大学
地点:雁栖湖校区 教1-109
自旋电子学是基于电子的自旋、轨道和点和自由度,研究电子自旋相关输运性质及自旋与磁、光、电、力 、热、声等物理场之间相互作用的新兴学科。21世纪将是自旋电子学交叉学科蓬勃发展和自旋电子器件深入开发及广泛应用的黄金时期。自旋电子器件将对计算机、物联网、人工智能、工业与民品、航空航天、深海探测、心磁脑磁成像与医疗检测、信息科学和技术等众多领域的发展起到巨大推动作用。该报告将简述新型磁性隧道结材料制备以及隧穿磁电阻效应、基于量子阱态的自旋共振隧穿磁电阻效应和新型磁子阀效应等物理研究,并简要介绍磁性隧道结及其隧穿磁电阻效应和新型磁子阀和磁子结效应等在自旋电子学核心器件方面的重要代表性应用与研究进展,例如磁随机存储器、自选逻辑/磁逻辑、TMR磁敏传感器、自旋共振隧穿二极管以及一类新型磁子阀和磁子结等关键器件等。
2How to talk to a mirror world?-- A new theory for solving the puzzles of dark matter, neutron lifetime, and star evolution
报告人:Wanpeng Tan
时间:2月26日(周二)10:30
单位:中科院物理研究所
地点:M楼830
A mirror sector of our universe has been conjectured since Lee and Yang published their seminar work on parity violation. There are many desirable features from such mirror matter that has been predicted. However, no concrete model was successful or compatible with our known universe. A new mirror-matter model is proposed under a spontaneously broken mirror symmetry, which results in oscillations of neutral particles. As it turns out, neutron-mirror neutron (n-n') oscillations become the best messenger between the ordinary and the mirror worlds. The new n-n' model resolves the neutron lifetime discrepancy, i.e., the 1% difference between measurements from "Beam" and "Bottle" experiments. The picture of how the mirror-to-ordinary matter density ratio is evolved in the early universe into today's observed dark-to-baryon matter density ratio (~5.4) is gracefully demonstrated. A new theory of evolution and nucleosynthesis in stars based on the new model of n-n' oscillations presents remarkable agreement between the predictions and the observations. For example, progenitor mass limits and structures for white dwarfs and neutron stars, two different types of core collapse supernovae (Type II-P and Type II-L), pulsating phenomena in stars, etc, can all be easily and naturally explained under the new theory. Further tests and applications of the new theory will be discussed as well.
3From the Cosmic Dawn to the Epoch of Reionization: a Radio Quest for Neutral Hydrogen in the Infant Universe
报告人:L.V.E. Koopmans,Kapteyn Astronomical Institute
时间:2月26日(周二)14:00
单位:清华大学
地点:蒙民伟科技南楼S727
4The Mu2e experiment at Fermilab
报告人:Yaqian Wang,Boston University
时间:2月27日(周三)10:00
单位:中科院高能物理所
地点: B326, main building
The Mu2e experiment will measure the charged-lepton flavor violating conversion of a negative muon into an electron. Compared to previous measurement, Mu2e is expected to improve the precision by four orders of magnitude. The experiment is sensitive to a wide range of new physics, complementing and extending other CLFV searches. we expect to start taking physics data in 2022 with 3 years of running.
5Bi-local Holography
报告人:Robert de Mello Koch,South China Normal University & University of the Witwatersrand
时间:2月27日(周三)10:30
单位:中国科学院理论物理所
地点:Room 6420, ITP NEW BUILDING
We present the basic ingredients in bi-local holography, which is a constructive scheme for reconstructing AdS bulk theories in the vector model / AdS duality. The mapping from CFT primaries to bulk AdS and higher spin fields is described and an all order non-linear collective action is given. This generates bulk Feynman (Witten) diagrams (at tree and loop level).
6Quantitative analysis of tensor effects in the relativistic Hartree-Fock theory
报告人:梁豪兆,RIKEN / University of Tokyo, Japan
时间:2月27日(周三)15:00
单位:中科院理论物理所
地点:Room 6420, ITP NEW BUILDING
The tensor force is one of the most important components of the nucleon-nucleon interaction and plays a critical role in the shell evolution in exotic nuclei. In particular, during the past decade, the experimental data on the shell evolution of nuclei far from the stability line bloomed a series of works focused on the corresponding tensor effects in both the nonrelativistic and relativistic density functional theories (DFT).
In a series of recent works, we identified the tensor force up to the 1/M2order in each meson-nucleon coupling in the relativistic Hartree-Fock (RHF) theory, by the nonrelativistic reduction for the relativistic two-body interactions. The effects of tensor force on various nuclear properties can now be investigated quantitatively, which eventually allows fair and direct comparisons with the corresponding results in the nonrelativistic framework.7粒子物理和宇宙学中的自发对称性破缺问题
报告人:舒菁,中科院理论物理所
时间:2月28日(周四)16:30
单位:清华大学
地点:理科楼郑裕彤讲堂
8Chemical Modeling of Interstellar Prebiotic Molecules: Ethanimine and Caynomethanimine (Special Seminar)
报告人:Donghui Quan,Eastern Kentucky Univ.
时间:3月1日(周五)14:00
单位:清华大学
地点:蒙民伟科技南楼S727
Despite the extremely low density and low temperature in the interstellar medium , the chemistry therein is surprisingly active. To date, more than 200 molecules, including many organic ones, have been detected in the interstellar medium. Some of these interstellar molecules are considered prebiotic molecules as they can serve as precursors of biological molecules such as amino acids . We have developed a series of models, including cold, warm-up and shock models, to study the chemical reactions of interstellar prebiotic molecules ethanimine and caynomethanimine isomers. By comparing the calculated abundances with the observed values, we studied in detail the formation and destruction mechanism, and pointed out the physical conditions of the corresponding regions. The study can enrich our understanding of astrochemistry, and may help to answer one of the human beings' ultimate question: the origin of life on the earth.
9 How to glue a spacetime from entanglement wedges
报告人:Bartek Czech,清华大学
时间:3月1日(周五)14:00
单位:中科院理论物理所
地点:Room 6420, ITP NEW BUILDING
If a holographic bulk spacetime is built out of quantum entanglement in the boundary theory, how do we understand the bulk connection? To inspect the entanglement structure of a boundary state, we dissect it into components and look at their quantum correlations. Each boundary component reconstructs a region of the bulk called entanglement wedge. The entanglement wedge (and its corresponding component subregion of the boundary) has an internal symmetry called modular flow, which has two properties that will be useful for our purposes. First, modular flow is a gauge symmetry because it relates to one another different ways of presenting the same physical system--the entanglement wedge. Second, modular flow is a generalization of choosing the phase of a pure quantum state in a Hilbert space. When we glue together two overlapping entanglement wedges to build a larger spacetime, we must specify how to map the observables in the first wedge (presented in some modular frame--in some gauge) to observables in the second wedge (also presented in some gauge). Thus, gluing together two component subregions of the boundary--as well as two entanglement wedges--requires a connection that relates their respective modular frames. This connection is analogous to specifying the phase of a quantum state that evolves under a time-dependent Hamiltonian, that is the Berry phase. I argue that the modular Berry connection is the boundary origin of the usual, geometric connection in the bulk. I will sketch some subtleties in the formal construction of the modular Berry connection, give examples and list key questions for the future.
更多报告信息:中国物理学会期刊网学术讲座列表
杨-米尔斯理论说了啥?为什么说这是杨振宁超越他诺奖的贡献?
利用胶体系统研究玻璃态(一)
天行见物理之二:其命维新
再见了,驻留在火星的伟大哨兵——机遇号!
宇宙膨胀背后的故事(之四):察颜观色识星移
轻巧灵动的未来
12个革命性的公式量子十问之四:“薛定谔猫”为什么会自然死亡?| 郭光灿
先生之风,山高水长 | 送别梁敬魁先生
雷达启发的强激光啁啾脉冲技术——军事需求催生基础研究的一个典型案例
那棵消失的树—回忆导师张首晟

来源:cpsjournals 中国物理学会期刊网
原文链接:https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s?__biz=MjM5NjYwNzM1Ng==&mid=2651595445&idx=1&sn=6500d10431f55ef00ffbcc8a1539e45c&scene=0#wechat_redirect
版权声明:除非特别注明,本站所载内容来源于互联网、微信公众号等公开渠道,不代表本站观点,仅供参考、交流、公益传播之目的。转载的稿件版权归原作者或机构所有,如有侵权,请联系删除。
电话:(010)86409582
邮箱:kejie@scimall.org.cn
Matter:淀粉颗粒让水凝胶刚柔并济

东南大学赵远锦团队《Matter》:仿生粘附结构色颜料

Matter: 五颜六色的刺激响应可擦写变色器件

北大张锦院士团队《Matter》:重叠晶界的原子尺度研究!
《Matter》:打破传统极限的颠覆性纳米制造技术!
《Matter》:金属锂电池人工界面研究领域研究进展

《Matter》:首次实现连续纤维增强热固性材料的3D打印

UCLA顾臻团队Matter:构建抗癌脂肪细胞
《Matter》:高度有序致密的导热石墨烯膜
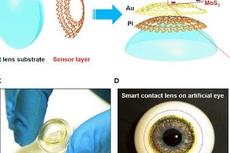
英国萨里大学赵云龙《Matter》:多功能智能隐形眼镜