科技工作者之家
科技工作者之家APP是专注科技人才,知识分享与人才交流的服务平台。
科技工作者之家 2020-12-27
来源:植物生物学
今天,介绍一篇综述文章,由中科院微生物所郭惠珊团队在《Current Opinion in Virology》发表的论文《Recent advances in understanding plant antiviral RNAi and viral suppressors of RNAi》。
植物-病毒的相互作用为了解宿主抗病毒免疫和病毒反防御机制提供了一个极好的模型。病毒衍生的小干扰RNA会在受感染的植物细胞内部触发主要的抗病毒防御机制,RNA会将依赖同源性的RNA干扰(RNAi)和/或RNA定向的DNA甲基化(RdDM)导向目标RNA和DNA病毒。
在反防御方面,植物病毒已独立进化出RNAi的病毒抑制子(VSR)以特异性拮抗抗病毒RNAi。最近的研究表明,植物抗病毒反应受到内源性小RNA,RNA衰变和自噬的调节,并且一些已知的植物RNA和DNA病毒的VSR也以这些新近被识别的防御反应为靶标来促进感染。
这篇综述着重于介绍这些最近的进展,这些进展揭示了植物-病毒相互作用的多层调节机制。
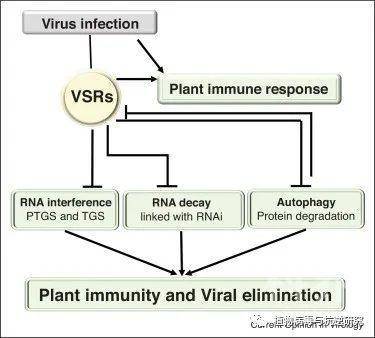
Molecular plant–virus interactions provide an excellent model to understanding host antiviral immunity and viral counter-defense mechanisms. The primary antiviral defense is triggered inside the infected plant cell by virus-derived small-interfering RNAs, which guide homology-dependent RNA interference (RNAi) and/or RNA-directed DNA methylation (RdDM) to target RNA and DNA viruses. In counter-defense, plant viruses have independently evolved viral suppressors of RNAi (VSRs) to specifically antagonize antiviral RNAi. Recent studies have shown that plant antiviral responses are regulated by endogenous small silencing RNAs, RNA decay and autophagy and that some known VSRs of plant RNA and DNA viruses also target these newly recognized defense responses to promote infection. This review focuses on these recent advances that have revealed multilayered regulation of plant–virus interactions.
来源:PlantBiotech 植物生物学
原文链接:http://mp.weixin.qq.com/s?__biz=MzI5NTk2MTcyOA==&mid=2247494456&idx=5&sn=65a099fe93187f4e089f115d59ea7d21
版权声明:除非特别注明,本站所载内容来源于互联网、微信公众号等公开渠道,不代表本站观点,仅供参考、交流、公益传播之目的。转载的稿件版权归原作者或机构所有,如有侵权,请联系删除。
电话:(010)86409582
邮箱:kejie@scimall.org.cn

揭示植物RNA病毒利用UPR-细胞自噬促进病毒侵染的新机制
2016年全国植物生物学大会在湖北武汉召开
科研人员揭示红光调控植物抗虫媒病毒新机制
2015上海辰山“药食同源与植物代谢”国际学术研讨会顺利召开
上海植物逆境中心研究组解析了植物病毒与宿主围绕Cajal体的博弈新机制
植物如何抵抗病毒?——植物干细胞广谱抗病毒机制
微生物所揭示红光调控植物抗虫媒病毒新机制

PNAS:植物DNA病毒在昆虫体内复制机制
植物逆境中心研究团队解析植物病毒与宿主围绕卡哈尔体的博弈新机制
2017国际植物日之--南开大学站成功举办