科技工作者之家
科技工作者之家APP是专注科技人才,知识分享与人才交流的服务平台。
科技工作者之家 2021-08-29
丝状真菌在侵染寄主过程中通过菌丝的延伸形成吸器,吸器结构可以帮助病菌分泌效应因子和获得养分【1,2】。侵染过程中,吸器的细胞外膜与寄主细胞质膜相连但是拥有不同的脂质和蛋白组分【3】。吸器可以分泌效应因子如致病疫霉分泌的RXLR类蛋白,RXLR类蛋白通过在吸器表面积累攻击宿主细胞,而宿主植物通过抗病基因抵抗毒力效应因子的分泌,符合经典的“基因对基因”学说【4,5】。大多数抗病蛋白家族属于NLR类,在植物与病菌互作过程中,NLR类蛋白主要定位在细胞质、质膜、细胞核以及液泡膜,发挥效应子识别、HR反应或其他免疫信号的传导,有些NLR类蛋白通过改变定位感知效应子并启动免疫反应【6-9】。但是,由于NLR类蛋白引起的HR反应造成剧烈的细胞死亡,侵染过程中NLR类蛋白的亚细胞定位变化尚未得到很好地研究。
近日,英国帝国理工学院科研人员在PNAS发表了题为Dynamic localization of a helper NLR at the plant-pathogen interface underpins pathogen recognition的研究论文,首次描述了NLR类蛋白在受感染植物细胞中时空定位的动态变化。


本研究中,研究人员利用致病疫霉—本氏烟互作体系,根据晶体结构学对抗病小体的研究,巧妙地使抗病NLR蛋白丧失引起细胞HR的能力,但是保留辅助蛋白的正常功能,通过活细胞成像技术探究了NLR类免疫相关蛋白在病害发生过程中的膜定位动力学变化。
该研究主要关注的是辅助免疫蛋白NRC4,发现该蛋白在病菌与宿主接触前,首先在吸器外膜(EHM)大量积累,而且该活动的完成需要完整的N端功能域。当病菌开始侵染时,激活后的NRC4不表现在EHM处积累,转而一定程度上在宿主质膜上形成斑点,说明发挥免疫功能的NRC4可能从激活位点扩散到其他质膜的位置。同时本研究中发现功能类似NRC4的NRC2和ZAR1免疫蛋白表现出不同的动力学变化,因此NRC4免疫蛋白的机制,在宿主与病原细菌、病毒、病原线虫、病原卵菌及蚜虫的互作中是否广泛存在需要进一步研究。
根据NRC4的动力学,研究人员认为在病菌侵染初期,免疫相关蛋白在新合成的植物-病原体界面膜上富集,来源于病菌的效应蛋白也主要部署在此处;当免疫反应发生后,激活的受体蛋白可能在细胞外围形成点状结构,进而从免疫激活部位逐渐扩散到其他质膜位点,极有可能促进了宿主的免疫。
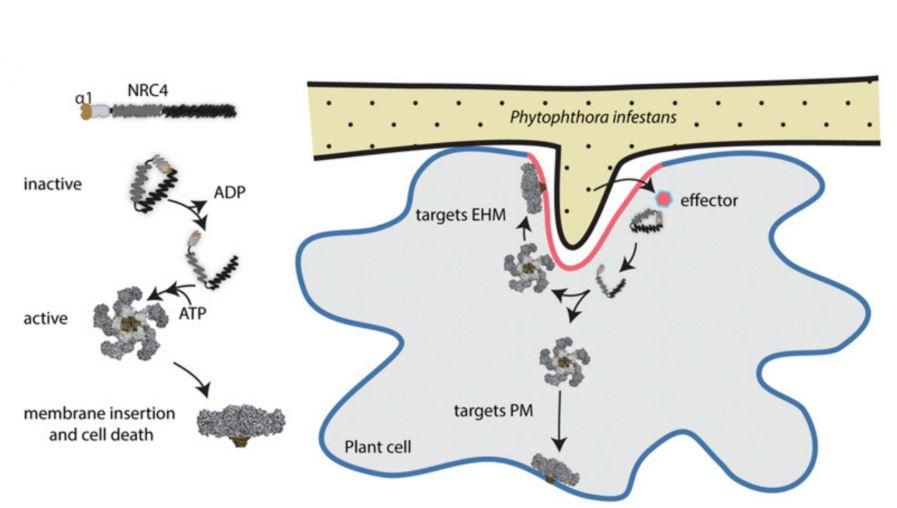
Model depicting possible modes of action of NRC4 where NRC4 gets activated via sensor NLRs (not shown) at the EHM by detecting perihaustorial effectors.
综上所述,该研究借助先进的活细胞成像技术,首次观察到NLR类抗病蛋白在病菌与宿主植物相互作用过程中的膜定位动力学变化,加深了人们对效应因子与宿主免疫蛋白互作的认识,为免疫蛋白发挥抗病功能的机制提供了新的思路和见解。
参考文献:
【1】S. Wang et al., Delivery of cytoplasmic and apoplastic effectors from Phytophthora infestans haustoria by distinct secretion pathways. New Phytol. 216, 205–215 (2017).
【2】S. Wang et al., The Phytophthora infestans haustorium is a site for secretion of diverse classes of infection-associated proteins. mBio 9, 1–14 (2018).
【3】T. O. Bozkurt et al., The plant membrane-associated REMORIN1.3 accumulates in discrete perihaustorial domains and enhances susceptibility to Phytophthora infestans. Plant Physiol. 165, 1005–1018 (2014)
【4】S. Wang et al., Phytophthora infestans RXLR effectors act in concert at diverse subcellular localisations to enhance host colonisation. J. Exp. Bot. 70, 343–356 (2018).
【5】D. G. O. Saunders et al., Host protein BSL1 associates with Phytophthora infestans RXLR effector AVR2 and the Solanum demissum Immune receptor R2 to mediate disease resistance. Plant Cell 24, 3420–3434 (2012).
【6】Z. Gao, E.-H. Chung, T. K. Eitas, J. L. Dangl, Plant intracellular innate immune receptor Resistance to Pseudomonas syringae pv. maculicola 1 (RPM1) is activated at, and functions on, the plasma membrane. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 108, 7619–7624 (2011).
【7】J. L. Caplan, P. Mamillapalli, T. M. Burch-Smith, K. Czymmek, S. P. Dinesh-Kumar, Chloroplastic protein NRIP1 mediates innate immune receptor recognition of a viral effector. Cell 132, 449–462 (2008).
【8】Q. H. Shen, et al., Nuclear activity of MLA immune receptors links isolate-specific and basal disease-resistance responses. Science 315, 1098–1103 (2007).
【9】S. Engelhardt et al., Relocalization of late blight resistance protein R3a to endosomal compartments is associated with effector recognition and required for the immune response. Plant Cell 24, 5142–5158 (2012).
原文链接:
https://www.pnas.org/content/118/34/e2104997118
来源:植物
原文链接:http://mp.weixin.qq.com/s?__biz=MzU3ODY3MDM0NA==&mid=2247510091&idx=2&sn=bdbd32aa423f55e408368fea2473a482
版权声明:除非特别注明,本站所载内容来源于互联网、微信公众号等公开渠道,不代表本站观点,仅供参考、交流、公益传播之目的。转载的稿件版权归原作者或机构所有,如有侵权,请联系删除。
电话:(010)86409582
邮箱:kejie@scimall.org.cn

研究发现病菌侵染植物的新机制
《生命科学》出版植物营养与人类健康专刊
2017国际植物日之--南开大学站成功举办

揭秘:植物如何在与病菌的斗争中取胜?

PLoS Pathogens:发现ABC蛋白调控赤霉病菌铁动态平衡的新机制
植物生理生态研究所科研人员发现植物抗虫调控新机制

研究发现:动物蛋白在维持人体肌肉上优于植物蛋白

植物蛋白饮料、植物奶、豆浆,跟牛奶有什么不同?

植物体内点“烽火”,搭建屏障拦病菌

“借力克敌制胜”,一个III型效应蛋白促进植物多胺合成,助力青枯病菌生存!