科技工作者之家
科界APP是专注科技人才,知识分享与人才交流的服务平台。
科技工作者之家 2020-01-30
来源:知社学术圈
金属纳米团簇常用于催化,因具有较高的分散性,应用领域不断扩大。与较大的金属纳米颗粒相比,其固有活性通常要高出数倍。这种高出的催化活性主要归因于其存在稳定的低配位位点,虽然也有其他相关效应的作用,如量子尺寸效应、表面张力诱导的应变、载体-金属相互作用。由于这些作用,纳米团簇的反应性,包括其优选的反应途径和中间体,会随其储存的微小变化直至添加或去除哪怕1个原子,都可能发生很大变化。纳米团簇反应性的这种可变性阻碍了相关理论突破,无法快速对团簇进行表征,也无法筛选出具有最佳催化性能的团簇。
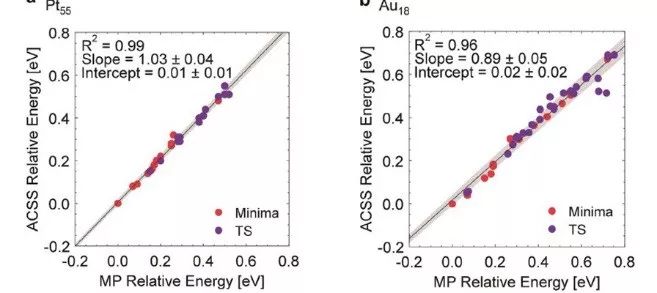
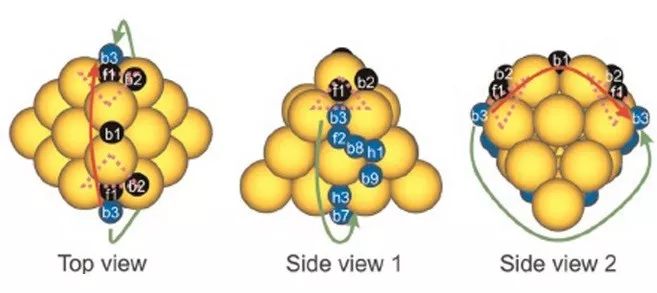
来自美国威斯康星大学麦迪逊分校化学与生物工程系的Manos Mavrikakis教授领导的小组,提出了这一自动化、可高度并行化的方法,来生成3D纳米团簇表面的近似2D的势能面(PES)(称为团簇表面自动扫描法,ACSS)。通过探测Au18和Pt55纳米团簇表面吸附氢原子的势能面,验证了该方法的准确性和高效性。他们之所以选择用Au18和Pt55纳米团簇为例,是因为在先前的实验结果发现,金和铂的小团簇在吸附表面H的各种催化过程中都是有活性的。他们首先通过与标准手动执行(MP)的计算对比,证明了用ACSS方法获得的稳定吸附位点和金属纳米团簇表面上任意两个位点的扩散路径;其次,他们对ACSS引入的误差做了量化,评估了ACSS中假设的有效性;最后,他们比较了ACSS法与MP方法的计算成本。以Au18和Pt55表面吸附原子H和扩散的测试作为实例,ACSS法定性和定量地重现了传统MP计算得到的结果,同时降低了计算成本。重要的是,计算成本的收益会随团簇的尺寸增大而急剧增加,而在这种情况下,凭人类直觉来预测吸附位点和扩散路径往往非常不可靠,且容易出错。
ACSS方法消除了如探测稳定的吸附位点和扩散势垒等繁琐、重复的任务。此外,它们消除了用户的人为错误,降低了遗漏潜在的重要吸附位点或扩散路径的可能性。由于该方法的通用性,可以预见它将成为实现大型模型纳米团簇复杂表面自动探测的基础。这类纳米团簇不仅在催化领域有技术应用,而且在化学和材料科学领域也有应用,例如分析吸附在复合电池正极材料表面和晶界上的扩散。作者所建立的方法可极大地加速新材料的发现和催化剂的合理设计。
该文近期发表于npj Computational Materials 5: 101 (2019),英文标题与摘要如下,点击左下角“阅读原文”可以自由获取论文PDF。
Identification of stable adsorption sites and diffusion paths on nanocluster surfaces: an automated scanning algorithm
Tibor Szilvási, Benjamin W. J. Chen & Manos Mavrikakis Article metrics
The diverse coordination environments on the surfaces of discrete, three-dimensional (3D) nanoclusters contribute significantly to their unique catalytic properties. Identifying the numerous adsorption sites and diffusion paths on these clusters is however tedious and time-consuming, especially for large, asymmetric nanoclusters.Here, we present a simple, automated method for constructing approximate 2D potential energy surfaces for the adsorption of atomic species on the surfaces of 3D nanoclusters with minimal human intervention. These potential energy surfaces fully characterize the important adsorption sites and diffusion paths on the nanocluster surfaces with accuracies similar to current approaches and at comparable computational cost.Our method can treat complex nanoclusters, such as alloy nanoclusters, and accounts for cluster relaxation and adsorbate-induced reconstruction, important for obtaining accurate energetics.Moreover, its highly parallelizable nature is ideal for modern supercomputer architectures. We showcase our method using two clusters: Au18 and Pt55.For Au18, diffusion of atomic hydrogen between the most stable sites occurs via non-intuitive paths, underlining the necessity of exploring the complete potential energy surface.By enabling the rapid and unbiased assessment of adsorption and diffusion on large, complex nanoclusters, which are particularly difficult to handle manually, our method will help advance materials discovery and the rational design of catalysts.
来源:zhishexueshuquan 知社学术圈
原文链接:https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s?__biz=MzIwMjk1OTc2MA==&mid=2247501382&idx=2&sn=0eaf21dfe4aad7848d89f7b6ac0c354d&chksm=96d438b9a1a3b1af14d8b19a58ed741e5932e399037ea29da4a39198391a22f4dce17cb7d078#rd
版权声明:除非特别注明,本站所载内容来源于互联网、微信公众号等公开渠道,不代表本站观点,仅供参考、交流、公益传播之目的。转载的稿件版权归原作者或机构所有,如有侵权,请联系删除。
电话:(010)86409582
邮箱:kejie@scimall.org.cn

中国微米纳米技术学会第十八届学术年会暨微系统与纳米工程高层论坛
纳米粒子自组装制备2D准纳米片
新法使用磁性纳米粒子治疗癌症

硅纳米粒子有助“曝光”肿瘤集聚区
纳米级厚度氧化铝涂层或可完美防腐

新型超分辨显微镜首次将DNA纳米结构形象化
多孔材料里,纳米粒子如何运动?
用x射线照射纳米粒子的生长?

医用纳米粒子可为农作物输送营养

合工大研发智能水凝胶,一分钟实现96%的自修复