科技工作者之家
科技工作者之家APP是专注科技人才,知识分享与人才交流的服务平台。
科技工作者之家 2020-05-12
来源:BioArt
撰文 | 小柚
责编 | 兮
组蛋白的翻译后修饰在真核细胞中发挥重要作用。其中,组蛋白H3第4位赖氨酸上的三甲基化(H3K4me3)是一类非常保守的且被广泛研究的表观遗传修饰。2001年,美国西北大学医学院的Ali Shilartifard【1】和德国德累斯顿工业大学的A.Francis共同鉴定了酵母中最早发现且唯一的H3K4甲基转移酶SET1及其复合物,并命名为COMPASS(COMplex of Proteins Associated with Set1)【2】。此后,COMPASS在果蝇【3】和哺乳动物中的同源蛋白也先后被鉴定。哺乳动物有6种COMPASS复合体,包含具有SET结构域的不同甲基转移酶。其中,SET1A/B介导细胞中的大部分H3K4me3修饰【4,5】,MLL3/4催化增强子处的H3K4me1【6-8】,而MLL1/2负责发育相关基因的H3K4me2和H3K4me3甲基化【9,10】。
MLL2基因对胚胎的早期发育是必需的,其突变会导致儿童肌张力障碍【11,12】。一般认为,H3K4me3富集在高表达的基因座位,与基因的激活表达相关,而越来越多的研究却发现敲低H3K4甲基化酶,只有少量基因的表达发生了变化【9,13,14】。因此,H3K4me3在基因调控中的功能还需进一步的研究。
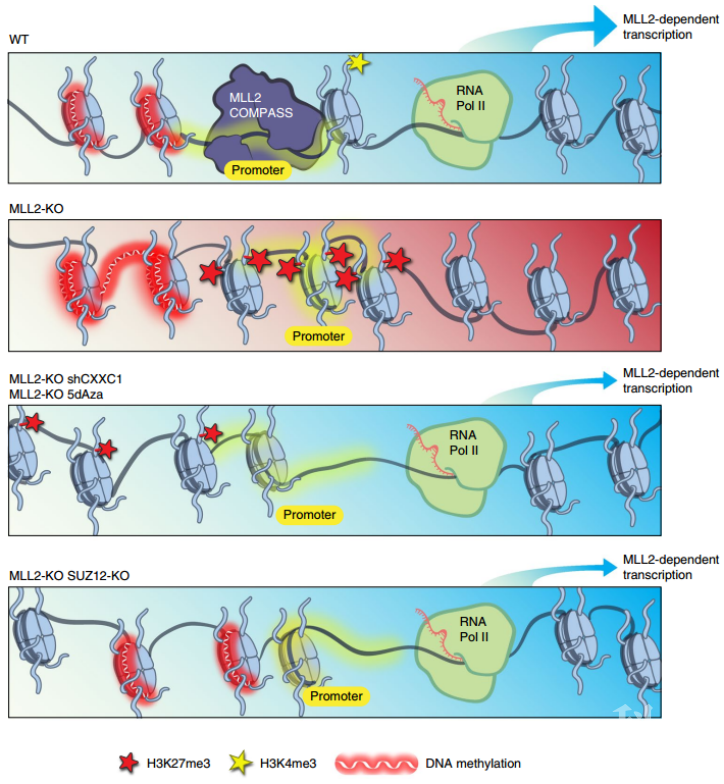
2020年5月11日,Ali Shilartifard教授在Nature Genetics发表研究Uncoupling histone H3K4 trimethylation from developmental gene expression via an equilibrium of COMPASS, Polycomb and DNA methylation,发现MLL2介导的H3K4me3通过拮抗转录异质性修饰H3K27me3和DNA甲基化,调控基因表达的机制。

Magohb是已知的受MLL2调控的基因,敲除MLL2导致Magohb的显著降低。为进一步理解MLL2如何调控基因表达,研究者在MLL2敲除的细胞系中构建了带mCherry标签的Magohb基因报告载体,再利用CRISPR进行全基因组筛选,寻找在MLL2缺失条件下,介导Magohb沉默的因子。通过该方法,研究者意外地发现敲低另一个COMPASS复合体SET1A/B,能够恢复MLL2敲除后导致的Magohb降低,说明SET1A/B参与了MLL2介导的转录调控。
同样是H3K4me3甲基化酶,为什么MLL2和SET1A/B对Magohb的调控竟是相反的呢?SET1A/B的缺失又是如何恢复由MLL2敲除导致的Magohb降低呢?值得注意的是,不仅Magohb,SET1A/B对其他MLL2依赖的基因也有相同的效果。
SET1A/B复合体可激活DNA 5mC甲基化酶DNMT1【15,16】,而DNA甲基化又与PRC复合体介导的H3K27me3修饰相关,因此研究者检测了敲低MLL2和SET1A/B后5mC和H3K27me3的变化。确实,敲低MLL2后,MLL2靶基因的5mC和H3K27me3显著升高,这与敲低MLL2后这些基因表达降低的现象相符,也说明MLL2缺失导致的基因表达抑制是由DNA甲基化和H3K27me3介导的。而SET1A/B的敲低显著降低DNMT1的表达,使得MLL2靶基因处的DNA甲基化和H3K27me3消失,恢复了这些基因的表达。
更重要的是,研究者发现H3K4me3,H3K27me3和DNA甲基化间的调控在胚胎分化过程中具有重要作用。使用DNA甲基化酶抑制剂5dAza(癌症治疗的临床用药)可解除MLL2缺失对基因表达的抑制,这提示5dAza有望用于MLL2突变造成的疾病。
总的来说,该研究进一步阐述了MLL2介导的H3K4me3的功能,揭示了H3K4me3,H3K27me3和DNA甲基化共同调控基因表达的机制。对MLL2的靶基因,MLL2介导的H3K4me3并不直接激活它们的表达,而是通过拮抗DNA甲基化和H3K27me3,解除这两种修饰对这些基因的抑制。值得注意的是,当抑制H3K27me3和DNA甲基化酶时,这些基因在缺乏H3K4me3的条件下依然可以表达,但其中的机制尚待进一步研究。
原文链接:
https://doi.org/10.1038/s41588-020-0618-1
参考文献
来源:BioGossip BioArt
原文链接:http://mp.weixin.qq.com/s?__biz=MzA3MzQyNjY1MQ==&mid=2652484455&idx=7&sn=695a7fcb02da034dab44a62e7d6ed3e9&chksm=84e220d3b395a9c567fed7f526926f2f184f16027a8b20f6d98c7c046439820dfd1bbb80605b&scene=27#wechat_redirect
版权声明:除非特别注明,本站所载内容来源于互联网、微信公众号等公开渠道,不代表本站观点,仅供参考、交流、公益传播之目的。转载的稿件版权归原作者或机构所有,如有侵权,请联系删除。
电话:(010)86409582
邮箱:kejie@scimall.org.cn
DNA甲基化跨代遗传研究取得进展

夜班影响:基因表达不能适应新的睡眠模式

当DNA甲基化遇上RNA甲基化:果实成熟的表观遗传调控
研究发现植物DNA主动去甲基化新机制

肠癌血浆DNA甲基化检测——数字PCR技术

当DNA甲基化遇上RNA甲基化:果实成熟的表观遗传调控

路超团队等揭示H3K36甲基化修饰与DNA甲基化修饰之间调控的内在机理
细胞重新编程,挖出皮肤愈合“超能力”
研究 | 成瘾行为形成的DNA甲基化调控机制
Nat Plants:植物如何防晒?抑制DNA甲基化