科技工作者之家
科技工作者之家APP是专注科技人才,知识分享与人才交流的服务平台。
科技工作者之家 2020-06-26
来源:土壤观察
导 读
香港理工大学土木及环境工程学系Daniel C.W. Tsang团队全面综述了微塑料的来源、转化和在土壤环境中的分布,讨论了微塑料对土壤生物群的相互作用和影响,并重点介绍了微塑料检测和定量方法的最新进展。相关成果发表于Environmental Pollution(IF=5.714)。
香港理工大学土木及环境工程学系Daniel C.W. Tsang团队全面综述了微塑料的来源、转化和在土壤环境中的分布,讨论了微塑料对土壤生物群的相互作用和影响,并重点介绍了微塑料检测和定量方法的最新进展。相关成果发表于Environmental Pollution(IF=5.714)。
Highlights
•Microplastics are considered as emerging persistent pollutants.
•Approximately 32% of plastics produced are available in terrestrial environments.
•Annually, 4.8–12.7 Mt of terrestrial plastic wastes enter the ocean.
•Sources, fate, and ecological risks of microplastics in soils are elaborated.
•Extraction and characterization methods of microplastics in soils are emphasized.
Abstract
Microplastics (MPs) as emerging persistent pollutants have been a growing global concern. Although MPs are extensively studied in aquatic systems, their presence and fate in agricultural systems are not fully understood. In the agricultural soils, major causes of MPs pollution include application of biosolids and compost, wastewater irrigation, mulching film, polymer-based fertilizers and pesticides, and atmospheric deposition. The fate and dispersion of MPs in the soil environment are mainly associated with the soil characteristics, cultivation practices, and diversity of soil biota. Although there is emerging pollution of MPs in the soil environment, no standardized detection and quantification techniques are available. This study comprehensively reviews the sources, fate, and dispersion of MPs in the soil environment, discusses the interactions and effects of MPs on soil biota, and highlights the recent advancements in detection and quantification methods of MPs. The prospects for future research include biomagnification potency, cytotoxic effects on human/animals, nonlinear behavior in the soil environment, standardized analytical methods, best management practices, and global policies in the agricultural industry for the sake of sustainable development.
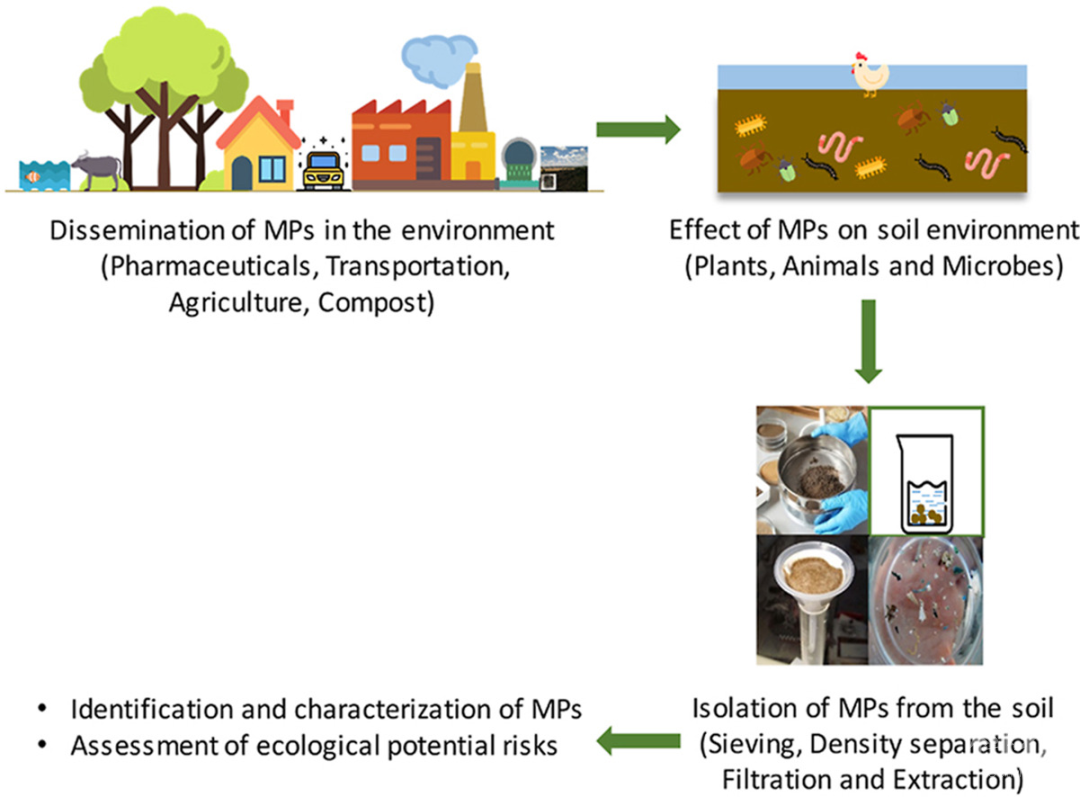
微塑料(MPs)作为一种新兴的持久性污染物已经成为全球日益关注的问题。尽管MPs在水生系统中得到了广泛的研究,但它们在农业系统中的存在和迁移转化还没有得到充分的了解。在农业土壤中,MPs污染的主要原因包括污泥和堆肥的使用、废水灌溉、地膜、聚合物基化肥和杀虫剂以及大气沉积。MPs在土壤环境中的转化和扩散主要与土壤特性、耕作方式和土壤生物多样性有关。虽然土壤环境中MPs正在出现污染,但目前还没有标准化的检测和定量技术。本研究全面综述了MPs的来源、转化和在土壤环境中的分布,讨论了MPs对土壤生物群的相互作用和影响,并重点介绍了MPs检测和定量方法的最新进展。对未来研究的展望包括生物放大效应、对人类/动物的细胞毒性效应、土壤环境中的非线性行为、标准化分析方法、最佳管理实践和农业可持续发展的全球政策。
来源:turangguancha 土壤观察
原文链接:https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s?__biz=MzA3MDMwNTExNg==&mid=2659319773&idx=1&sn=efccf60dc1c9c4e61e8b605cfc83b954&chksm=844b8beeb33c02f8865fc2663d750be8683ae641c3d96dbfee253cdff02bdae4251b24d22905#rd
版权声明:除非特别注明,本站所载内容来源于互联网、微信公众号等公开渠道,不代表本站观点,仅供参考、交流、公益传播之目的。转载的稿件版权归原作者或机构所有,如有侵权,请联系删除。
电话:(010)86409582
邮箱:kejie@scimall.org.cn
土壤动物肠道微生物的生态学功能方面研究获进展

新型微流控芯片可现场快速定量检测土壤养分离子

新型萤光生物传感器可以实现水和土壤样本中的草甘膦即时检测

农民对土壤的理解:对英国土壤保持和可持续农业的影响

【论文精选】超声波技术检测不同干湿交替条件下的土壤含水率

行业专家深度“点评”我国土壤污染治理情况和土壤修复
地化所建立基于生物传感器的土壤重金属检测系列新方法

城市环境所在水稻土厌氧铁铵氧化过程研究方面取得进展|研究

微塑料:一场不知不觉的污染
河北大学刘微团队:土壤中微塑料检测技术及生态风险研究进展