科技工作者之家
科技工作者之家APP是专注科技人才,知识分享与人才交流的服务平台。
科技工作者之家 2019-09-02
来源:知社学术圈
能够以给定原子坐标、给出原子系统势能的势能面(PES)是原子模拟方法的基础。原则上,求解薛定谔方程的从头算或第一原理方法,通常是Kohn-Sham密度泛函理论框架内的一些近似,可用于直接计算PES。虽然这些方法非常准确,并且可适用于多元素和复杂化学键体系,但其高计算成本限制了其在大规模分子动力学模拟中的应用,即难以实现包含数百个原子和亚纳秒时间尺度的动力学模拟。此时,传统的、具有参数化的经验势是一种较为便宜的替代方案。其函数形式大大简化,只需拟合几个参数即可进行动力学模拟。然而,经验势中描述长程静电相互作用的准确性必然受到势函数模型的近似,通常难以正确描述不同键合类型的复杂系统。
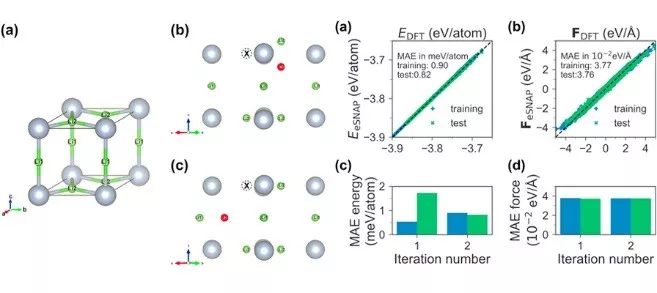
来自美国加州大学圣迭戈分校的Shyue Ping Ong教授领导的团队利用局部环境描述符,如邻域分析电势(eSNAP),证明了通过引入长程静电相互作用可适用于快离子体系的最新势函数。他们应用eSNAP模型对复杂的α-Li3N模型(500~5000个原子)进行了长时间(~1 ns)的模拟。他们发现通过直接计算电荷扩散系数和颗粒边界得到的α-Li3N的Haven比率在晶界处具有更快的扩散通道(相对于块体材料)。电荷扩散率的计算在从头算分子动力学模拟中非常难以收敛,而该参数的计算可使他们能够估算出更加可靠的α-Li3N各向异性扩散系数。有趣的是,尽管他们发现c方向的电导率通常比ab平面的电导率低,但与单晶的测量结果相比,电导率仅低一个数量级。该研究提供了一种在SNAP形式下发展多组分离子体系的量子精确力场的方法,为此类体系的大规模原子模拟提供了可能。
该文近期发表于npj Computational Materials 5: 75 (2019),英文标题与摘要如下,点击左下角“阅读原文”可以自由获取论文PDF。
An electrostatic spectral neighbor analysis potential for lithium nitride
Zhi Deng, Chi Chen, Xiang-Guo Li & Shyue Ping Ong
Machine-learned interatomic potentials based on local environment descriptors represent a transformative leap over traditional potentials based on rigid functional forms in terms of prediction accuracy. However, a challenge in their application to ionic systems is the treatment of long-ranged electrostatics. Here, we present a highly accurate electrostatic Spectral Neighbor Analysis Potential (eSNAP) for ionic α-Li3N, a prototypical lithium superionic conductor of interest as a solid electrolyte or coating for rechargeable lithium-ion batteries. We show that the optimized eSNAP model substantially outperforms traditional Coulomb–Buckingham potential in the prediction of energies and forces, as well as various properties, such as lattice constants, elastic constants, and phonon dispersion curves. We also demonstrate the application of eSNAP in long-time, large-scale Li diffusion studies in Li3N, providing atomistic insights into measures of concerted ionic motion (e.g., the Haven ratio) and grain boundary diffusion. This work aims at providing an approach to developing quantum-accurate force fields for multi-component ionic systems under the SNAP formalism, enabling large-scale atomistic simulations for such systems.
来源:zhishexueshuquan 知社学术圈
原文链接:http://mp.weixin.qq.com/s?__biz=MzIwMjk1OTc2MA==&mid=2247499097&idx=2&sn=813027d80e056e4b421b5f576cb19353&chksm=96d403a6a1a38ab02b2166a0993a85342cfeb1a5e41d1e6aeadcc1526a1a8defd6aba57084c0&scene=27#wechat_redirect
版权声明:除非特别注明,本站所载内容来源于互联网、微信公众号等公开渠道,不代表本站观点,仅供参考、交流、公益传播之目的。转载的稿件版权归原作者或机构所有,如有侵权,请联系删除。
电话:(010)86409582
邮箱:kejie@scimall.org.cn

今日科技话题:“大洋一号”船、 “向阳红10”船凯旋、“天河工程”卫星及火箭研制项目启动、有机太阳能电池转化光电率最高纪录
飞轮电池


水果电池

为什么锂电池会变身"定时炸弹"?这天生"爆"脾气的电池,你还敢用吗

关注 | Nature& Science:8月材料领域科研成果汇总 国内进账3篇
射线电池
混合电池

未来电池产业瞄准全固态电池
电池腐蚀
伽凡尼-燃料电池混合电池